Sexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Menstrual Cycle, Fertilization, Zygote, Parthenogenesis, Gametogenesis, Endogamy, Oestrus Cycle, Oviparous Animals, Viviparous Animals, Syngamy, Embryogenesis, External Fertilisation, Internal Fertilisation and, Isogamy
Important Questions on Sexual Reproduction
In which of the following phases all organisms have to pass through it before they can reproduce sexually?
Which of the following hormones play important role in menstrual cycle?
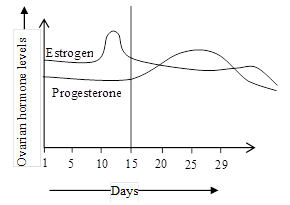
Read the graph given below and identify the period of follicular phase:
Both male and female reproductive structures are present on same plants in –
Read the following statements and select the wrong ones:
I. Juvenile phase is the pre-reproductive phase in the life cycle of an organism.
II. Bamboo species flower only once in their lifetime.
III. Mammals are called continuous breeders.
IV. In the oestrous cycle, broken endometrium is passed out.
When the male and female are morphologically different, the condition is called:
Development of new organism without fertilization of female gamete is called
Organisms showing internal fertilisation shows reduction in number of --------gamete and increase in number of ---------gamete.
Exogamy in plants is the term where pollination takes place between flowers of the same plant.
Exogamy is also called as _____.
Differentiate between exogamy and endogamy.
What is the carrier of  gamete in the Pinus, Marchantia, Mango, Chara, and Funaria respectively?
gamete in the Pinus, Marchantia, Mango, Chara, and Funaria respectively?
[where Pollen tube, ]
Synchrony between the maturity of sexes and release of many gametes is shown by:
Clear cut distinction between vegetative, reproductive and senescent phase is shown by
Pollen grains are the carrier of male gametes in
Majority of sexually reproducing organisms form
What would be the number of chromosomes in the meiocyte and gamete of onion respectively?
